Farley-CNC plasma cutting technology
Many plasma cuts are ionized by a high velocity gas stream ejected at a nozzle at a high temperature to form an electrical conductor. When a large current is passed, the conducting gas stream forms a high-temperature plasma arc, the heat of the arc locally melting (and evaporating) the metal at the workpiece slit, and a method of removing the molten metal by the power of the high-speed plasma gas stream to form a slit. The elongated and stable plasma arc formed by the annular airflow technique ensures that any conductive metal can be cut smoothly and economically.
The ion arc energy intensity of a fine plasma is three times that of a conventional plasma system. Combined with an improved torch, fine plasma gives the user nearly vertical edge cutting and the ability to cut complex shapes. Although limited by plasma arc slitting and fluency, fine plasma cutting is not as precise as laser, but there is no absolute advantage in laser cutting for many types of parts, and the cost of fine plasma cutting systems is much lower. The cost of a laser cutting system.
Many of the latest 260 amp fine plasma system sheet metal cutting speeds are close to the cutting speed of a 400 amp conventional plasma system. From thin metal sheets to 32mm thick metal sheets, the fine plasma cutting system achieves slag-free cutting. It is suitable for bevel cutting up to a 45 degree angle and can be cut underwater. While improving the cutting quality and cutting speed, the service life of plasma consumables has also been significantly improved. According to the customer feedback from Farley, a set of consumables can complete more than 3,000 cutting tasks.
Many plasma cuttings cut all sheet metal and many non-metallic materials with a maximum cutting speed of 10m/min, which is 10 times that of flame cutting. Underwater cutting can eliminate noise, dust, harmful gases and arcs generated during cutting, which is conducive to environmental protection.
Plasma cutting is especially suitable for medium and thick boring processing, such as shipbuilding, metallurgy, boiler containers, petroleum pipes and other industries.
Right Angle Prisms are used to direct beams at 90 degrees by using hypotenuse face in total internal reflection (TIR). The right angle prisms are often preferable to an inclined Mirror in applications involving severe acoustic or inertial loads, because they are easier to mount, and deform much less than mirror in response to external mechanical stress. As long as acceptance angle limitations for TIR from the roof faces are not exceeded, the right angle prisms can serve as a retro reflector, turning beams back to the original direction.
Available in sizes ranging from 3 mm to 60 mm, Right-Angle Prisms can be used to deviate a light path by 90° or 180°, depending on which surface is used as the input for the light source.
Right angle prisms are used to redirect light beams at 90 degrees. Right angle prisms are made of BK7, UVFS optical materials.
- 45-45-90 degree prisms
- Can be used as internal or external reflectors or as retro - reflector
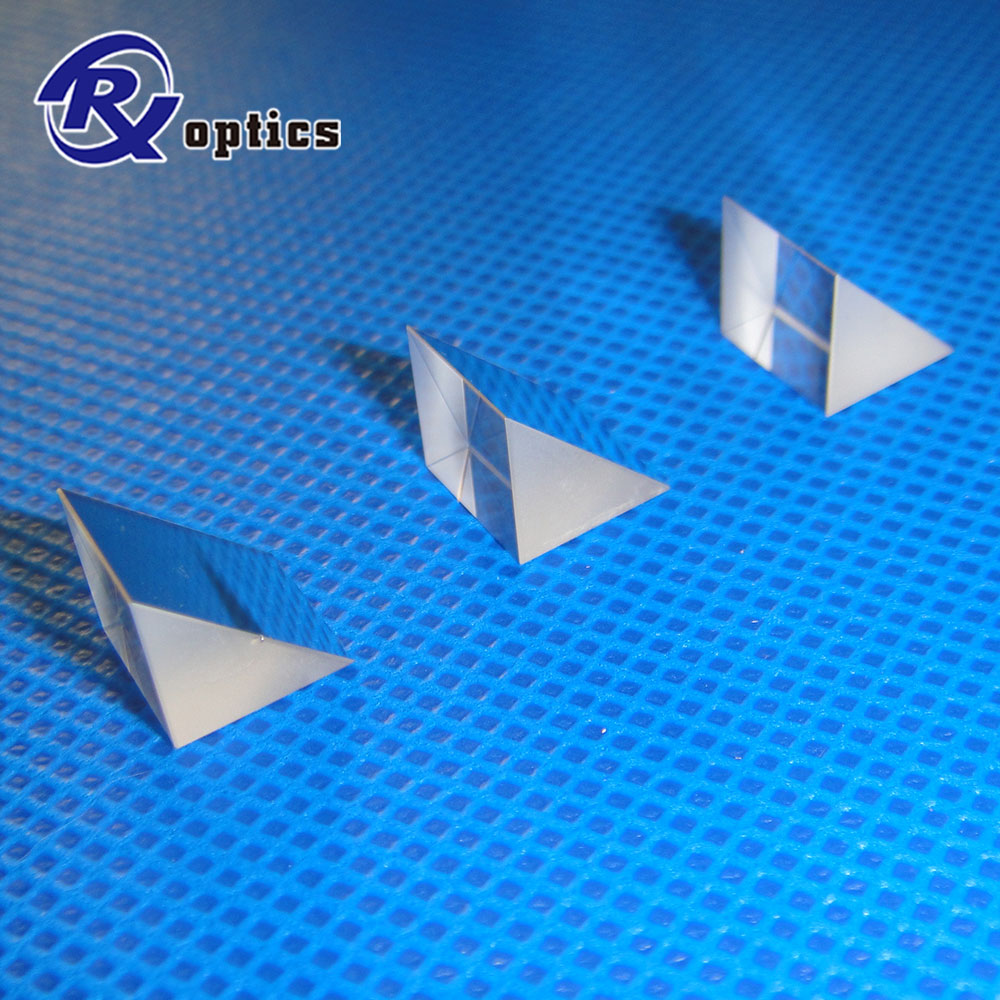
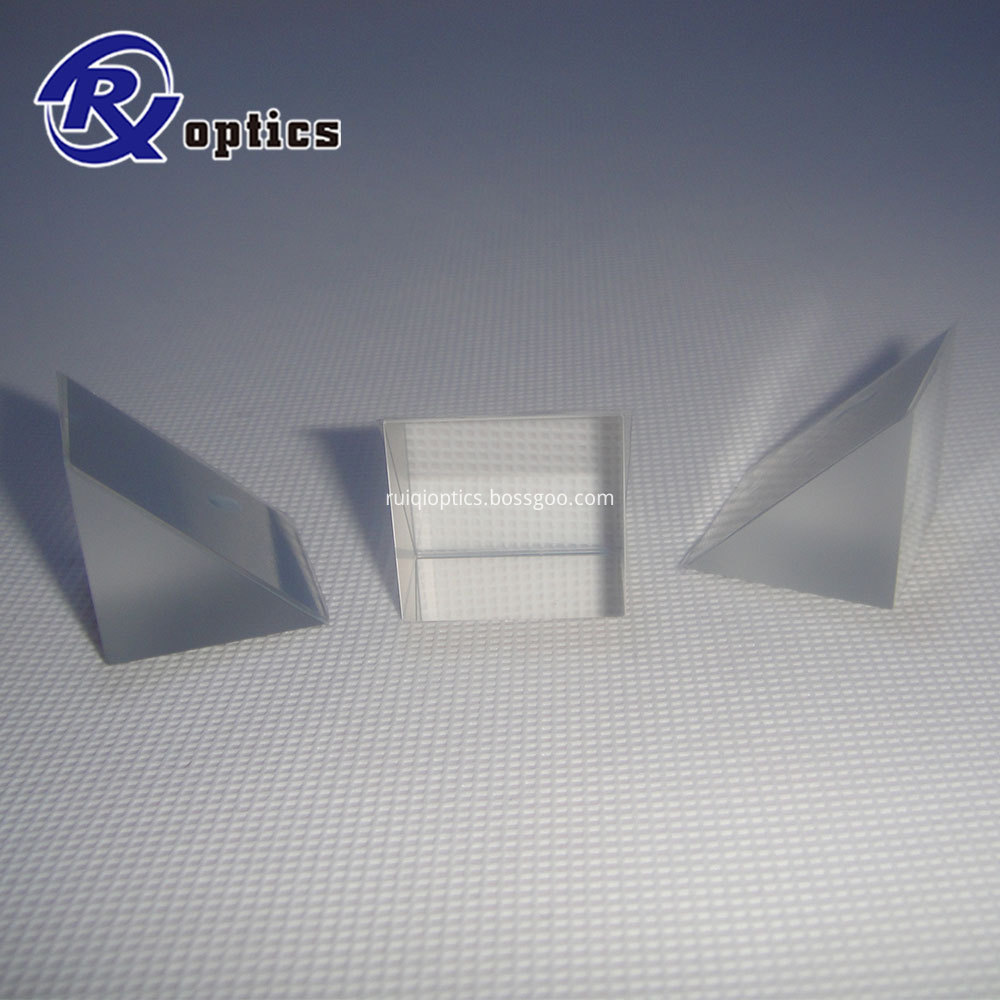
Right Angle Prisms
Right Angle Prisms,Glass Right Angle Prisms,Right Angle Prism Mirror,Right Angle Glass Prism
Changchun Ruiqi Optoelectronics Co.,Ltd , http://www.ruiqi-optics.com